GST was introduced in India in July 2017. This has brought various changes in Indian tax system. Reverse charge means the liability to pay the tax by person receiving goods/services instead of person supplying the goods/services in respect of specified categories of supplies. Reverse charge was under the service tax which has been introduced in GST. Under GST reverse charge may be applicable for both services and goods. Although right now there is no reverse mechanism in supply of goods.
Need for reverse charge under GST
Reverse charge’s aim is to increase tax compliance and tax revenues. Under earlier law the government was not able to collect service tax from various unorganised sectors like goods, transport etc. Thorough this mechanism compliances and tax collections will be increased.
For Example: Company A is providing services to company B if the bill charged is of ₹1,00,000 and suppose tax liability is of ₹15,000. So, the service provider company A will send bill of ₹1,00,000 and after mentioning that the service tax will be borne by receiver. So, company B will pay ₹1,00,000 to Company A and will deposit ₹15,000 to the government.
One can compare the direct charge Mechanism under GST and reverse charge mechanism under GST:
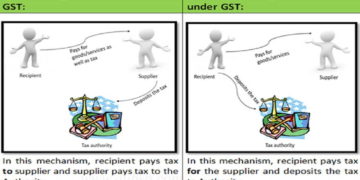
Direct Charge Mechanism under GST:
Direct Charge Mechanism under GST:In this mechanism, recipient pays tax to supplier and supplier pays tax to the Authority.
Reverse Charge Mechanism under GST:
In this mechanism, recipient pays tax for the supplier and deposits the tax to Authority.
When reverse charge is applied:
It can be applied in following circumstances:
- When unregistered dealer is selling goods to registered dealer. The registered dealer is required to pay GST on reverse charge basis for such supply.
- On services. There are 12 services notified by CBEC on which tax will be paid by recipient on 100% reverse basis:
- Non-resident service provider
- Goods Transport Agencies
- Legal service by an Advocate/ Firm of Advocates
- Arbitral Tribunal
- Sponsorship Services
- Specified Services provided by Government or Local Authority to Business entity
- Services of a director to a company
- Insurance agent
- Recovery Agent of Bank/FI/ NBFC
- Transportation Services on Import
- Permitting use of Copyright
- Radio Taxi services to E-commerce aggregator (e.g.: Ola, Uber, etc.)
Provisions for reverse charge under GST
Reverse Charge GST Registration:
The central government has issued a Notification No. 5/2017 dated 19th June 2016 exempted such persons from obtaining registration who are engaged in making supplies of taxable goods/services only. It is enforced on 22nd June 2016.
Invoicing Rules:
Taxpayer who is paying tax on basis of reverse charge has to mention this fact in his tax invoice that is being issued. The buyer or the person who is liable to pay tax under reverse charge has to mandatorily issue an invoice for goods/services received by him from unregistered supplier.
Exemption under GST:
The taxpayers who are paying the taxes on reverse charge under GST are not eligible for the exemption of threshold of ₹20 lakh in a financial year.
Composition scheme under GST:
There is Composition scheme for the small scale taxpayer who have aggregate turnover of ₹75 lakh in financial year. But this scheme is not available for the taxpayers paying tax under reverse charge.
Time of supply:
Under the reverse charge the time for supply of Goods should be earliest of the following dates:
- Date of the receipt of goods, or
- Date on which the payment is made, or
- Date immediately after 30 days from the date of issue of the invoice by the supplier (30 days for goods), or
- Date of debit in the books of accounts.
Under the reverse charge the time for supply of Services should be earliest of the following dates:
- Date of the receipt of services, or
- Date on which the payment is made, or
- Date immediately after 60 days from the date of issue of the invoice by the supplier (60 days for services), or
- Date of debit in the books of accounts.
