The Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies (BAMES) is an interdisciplinary undergraduate degree that combines in-depth study of the Middle East and North Africa’s history, politics, cultures, religions, and economics with intensive language training—most commonly Arabic, but also Hebrew, Persian, or Turkish—to prepare graduates for globally oriented careers.
Typically completed in 3–4 years, the program emphasizes critical thinking, research, and cross-cultural competence, often including study-abroad experiences, and leads to career paths in diplomacy, international organizations, journalism, NGOs, government and intelligence, international business, education, and translation.
While a BAMES degree offers strong employment prospects and starting salaries around $58,000 with higher potential over time, success depends heavily on achieving advanced language proficiency, gaining internships and regional experience, and often pursuing a master’s degree for senior or government roles, making it best suited for intellectually curious, globally minded students committed to language learning and flexible career trajectories.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Degree Name | Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies (BAMES) |
| Degree Level | Undergraduate |
| Duration | 3–4 years (3 years UK, 4 years US) |
| Study Mode | Full-time (on-campus; some hybrid options) |
| Core Focus | History, politics, culture, religion, economics of the MENA region |
| Language Requirement | Mandatory (Arabic most common; also Hebrew, Persian, Turkish) |
| Language Study Length | 2–3 years (often with study abroad) |
| Study Abroad | Strongly encouraged or required |
| Typical Curriculum | Middle Eastern history, politics, Islam, foreign policy, culture, advanced language study |
| Entry Requirements | High school diploma, GPA ~3.0+, English proficiency (IELTS/TOEFL), SAT/ACT (US) |
| Average Starting Salary | ~$58,000 (US average) |
| Salary Range | $45,000–$85,000+ depending on sector |
| Employment Outlook | Strong with language proficiency; very strong with MA |
| Common Career Paths | Diplomacy, NGOs, journalism, government, business, intelligence, education |
| Best For | Globally minded students interested in language, culture, and international affairs |
| Advancement | Master’s degree often required for senior/government roles |
Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies (BAMES): Complete Guide 2026-2027
The Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies (BAMES) is an increasingly popular undergraduate degree for students passionate about one of the world’s most dynamic and strategically important regions. Whether you’re interested in international diplomacy, journalism, business, or academia, a BAMES degree opens doors to careers that genuinely make a difference in global affairs.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about pursuing this degree—from what you’ll actually study to realistic salary expectations and career prospects across the globe.
What Is a Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies?
A Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies is an interdisciplinary undergraduate program that examines the history, politics, culture, economics, and religions of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. The degree combines rigorous academic study with practical language skills, typically requiring students to achieve proficiency in Arabic, Hebrew, Persian, or Turkish.
Unlike narrowly focused degrees, BAMES programs emphasize comprehensive regional understanding through multiple disciplinary lenses—including history, political science, economics, religious studies, anthropology, and sociology. This interdisciplinary approach makes graduates exceptionally adaptable professionals capable of tackling complex global challenges.
Typical Program Duration: 3-4 years (varies by country and institution)
Program Type: Full-time, undergraduate
Study Mode: On-campus (though many universities now offer hybrid options)
BAMES Program Structure and Curriculum
Core Coursework
Most Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies programs follow a similar structure with some institutional variation:
Year 1 (Foundational Studies)
- Introduction to Middle Eastern History
- Fundamentals of Islam and Islamic Civilization
- Contemporary Middle East Politics
- Introduction to Arabic/Hebrew Language
- Regional Geography and Economics
Years 2-3 (Advanced Studies)
- Middle Eastern Foreign Policy
- Islamic Law and Society
- Arab Culture and Literature
- Modern Middle Eastern History
- Advanced Language Studies
- Electives in specialized areas (Palestinian studies, Gulf politics, Islamic art, etc.)
Capstone/Honors Project
- Research thesis or independent project
- Typically 30 credits in final year
- Based on original research or analysis
Language Requirements
Language study is fundamental to BAMES programs. Most universities require students to complete 2-3 years of study in a Middle Eastern language, with options including:
- Modern Standard Arabic (most common)
- Hebrew
- Persian (Farsi)
- Turkish
- Kurdish
Universities like the University of Exeter and SOAS allow students to develop advanced proficiency, reaching levels where they can read academic texts, conduct interviews, and engage in sophisticated cultural analysis.
Top Universities for Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies
University Cost vs. Rankings Chart: – Compares 14 universities showing the relationship between tuition costs and rankings, helping international students identify value options.
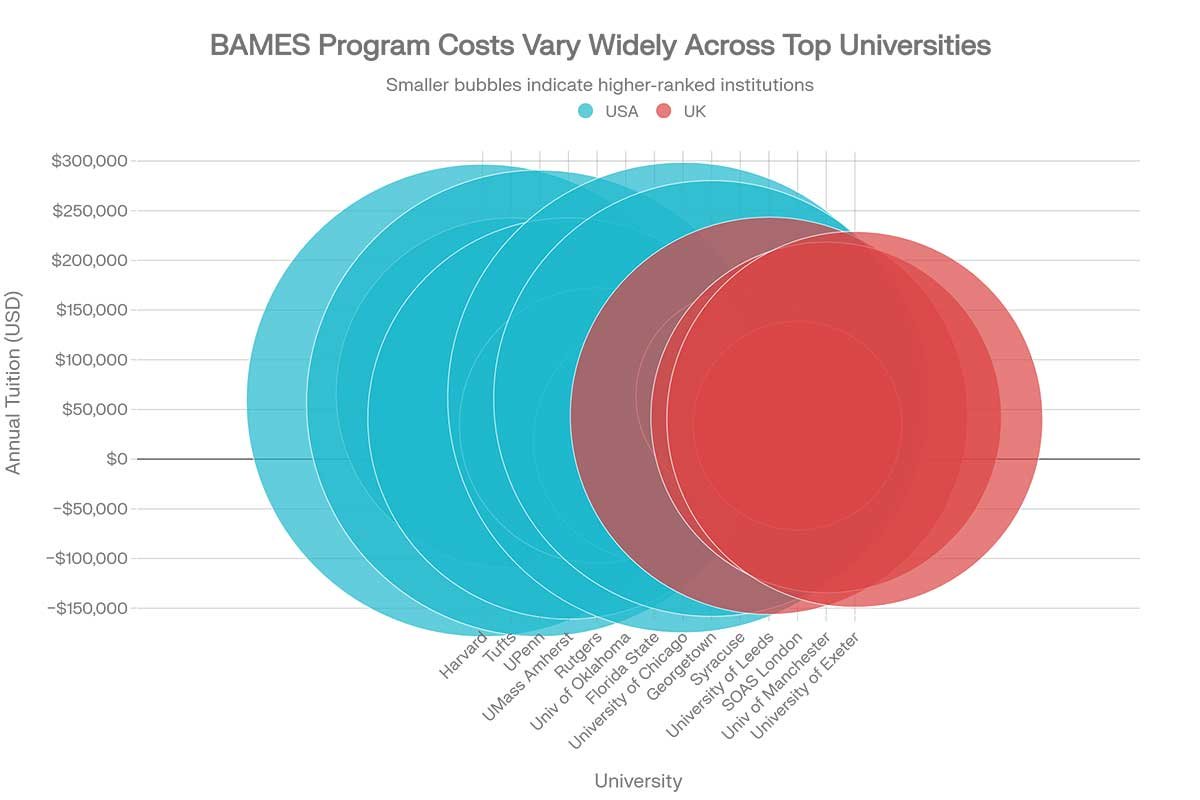
United States
| University | Location | Program Length | Tuition (Annual) | Acceptance Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvard University | Cambridge, MA | 2-year MA | $59,000 | 3% |
| University of Pennsylvania | Philadelphia, PA | 4 years | $56,200 | 5% |
| Tufts University | Medford, MA | 4 years | $66,600 | 9.7% |
| UMass Amherst | Amherst, MA | 4 years | $40,900 | 42% |
| University of Chicago | Chicago, IL | 4 years | Varies | 7% |
| Rutgers University | New Brunswick, NJ | 4 years | $33,800 | 65% |
| University of Oklahoma | Norman, OK | 4 years | $31,600 | 77% |
| Florida State University | Tallahassee, FL | 4 years | $18,700 | 25% |
United Kingdom
| University | Location | Program Length | Tuition (International) | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Leeds | Leeds | 3 years | £32,750 ($43,600) | #118 THE |
| University of Manchester | Manchester | 3 years | Varies | Top Tier |
| University of Exeter | Exeter | 3 years | Varies | Strong |
| SOAS, University of London | London | 1-year MA | £25,320 ($33,700) | #401 THE |
| University of Edinburgh | Edinburgh | 3 years | Varies | Top Tier |
Program Comparison: Key Differences
Ivy League Universities (Harvard, UPenn, Tufts) offer prestige and extensive resources but are highly competitive. Tuition exceeds $56,000 annually.
UK Universities offer 3-year programs (vs. 4 years in the US), making them cost-effective for international students despite high per-year fees. The UK system integrates language study more extensively.
Public US Universities (Florida State, University of Oklahoma, Rutgers) provide affordable options with strong Middle Eastern Studies departments. Tuition ranges from $18,700-$33,800 annually.
Admission Requirements for BAMES Programs
Academic Prerequisites
High School Qualifications (International Students):
- Strong GPA (typically 3.0 or equivalent)
- Strong performance in humanities subjects
- English proficiency (TOEFL/IELTS for non-native speakers)
Standardized Tests:
- SAT (US universities): Typically 1300-1560
- ACT (US universities): Competitive scores
- IELTS (UK/International): 6.0-7.0 band
- TOEFL (International): 90-104
- IB (International Baccalaureate): 30-32 points
Language Requirements
Most programs do not require pre-existing Arabic, Hebrew, or Persian knowledge. However, strong motivation to develop language skills is essential. Some universities offer language pathway programs for students without prior study.
Application Materials
- Academic transcripts
- Personal statement/essay
- Letters of recommendation (typically 2-3)
- Resume/CV
- English language proficiency test scores
- Portfolio or writing samples (some institutions)
Key Admission Factors
Universities weight applications holistically, considering:
- Academic strength (most important)
- Demonstrated interest in Middle Eastern region/culture
- Language aptitude (if relevant)
- Extracurricular activities (study abroad experience, language clubs, debate)
- Personal background and perspective
- Writing ability (essay quality)
BAMES Degree Career Prospects and Job Market 2026-2027
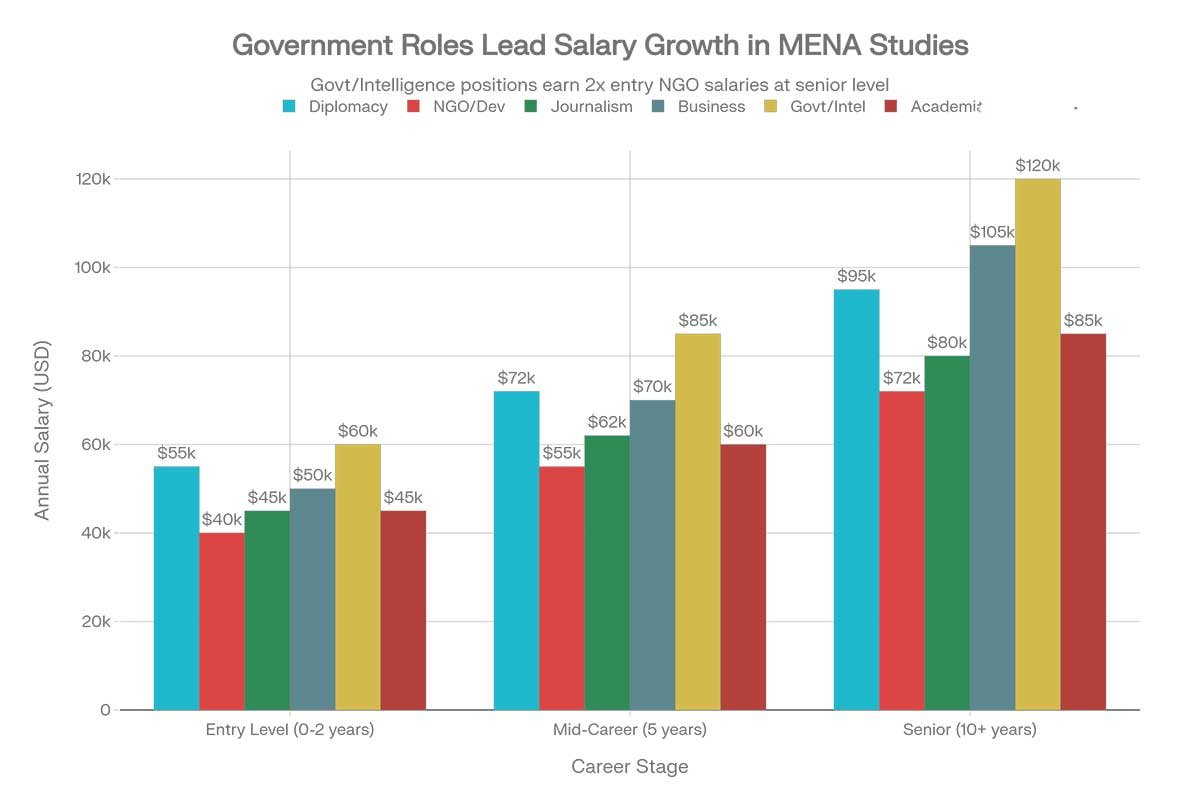
Employment Statistics
Recent data shows strong employment prospects for BAMES graduates:
- 100% employment rate for MA graduates in Arab Studies (Georgetown, Class of 2023)
- Average starting salary (US): $58,030 annually
- Salary range: $48,500 – $66,500 (25th-75th percentile)
- Top earners: $76,000+ within first 5 years
- Unemployment rate: Less than 2.4% for master’s degree holders vs. 5.4% for high school only
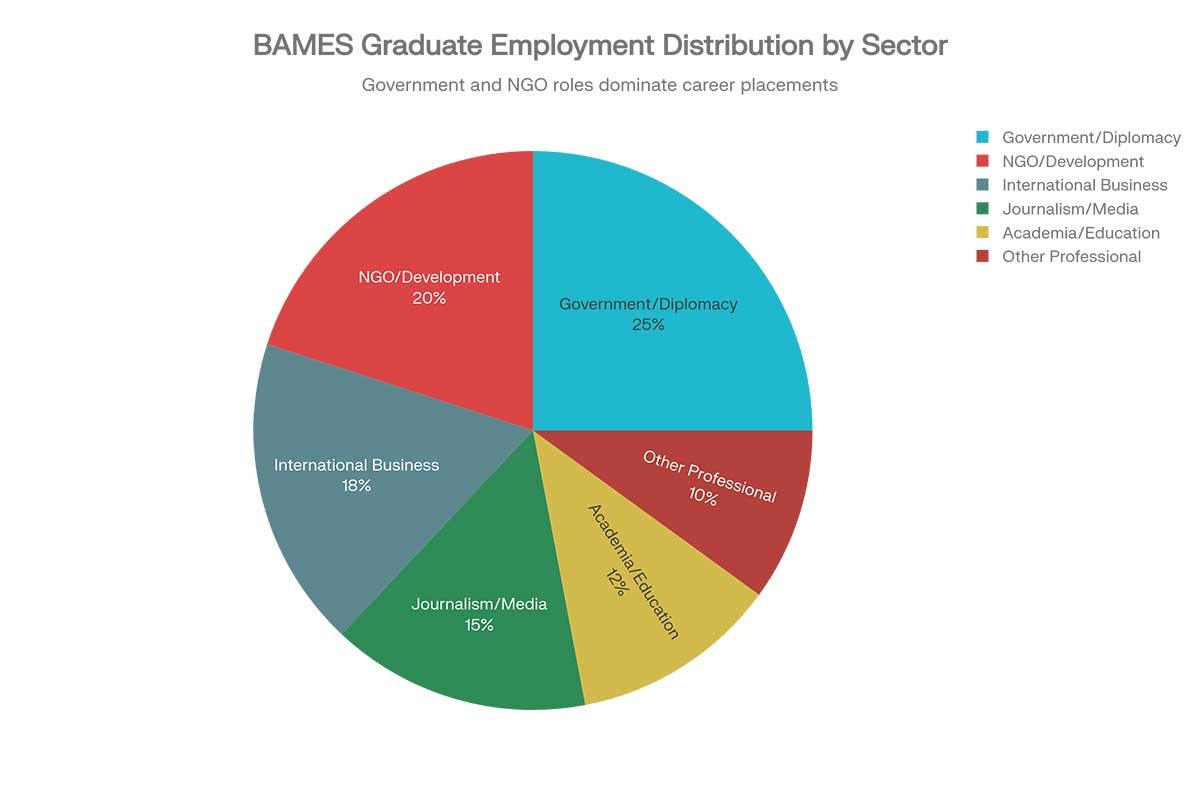
Top Career Paths for BAMES Graduates
Employment Sector Distribution Chart: – Pie chart showing where BAMES graduates actually work (Government 25%, NGO 20%, Business 18%, Journalism 15%, Academia 12%, Other 10%).
1. Diplomacy and International Relations
Graduates work with the U.S. State Department, United Nations, World Bank, and other international organizations. These roles typically require a master’s degree for advanced positions but offer meaningful work in foreign policy, development, and humanitarian affairs.
Typical Roles:
- Foreign Service Officer
- UN Policy Analyst
- Development Specialist
- International Relations Officer
Average Salary: $55,000-$80,000+ (entry-level to mid-career)
2. Journalism and Media
BAMES graduates work as journalists, editors, researchers, and producers for major news organizations including BBC, Reuters, Al Jazeera, and The Guardian. Language skills and regional expertise make them invaluable for international news coverage.
Typical Roles:
- Foreign Correspondent
- News Researcher
- Editor/Producer
- Documentary Producer
Average Salary: $45,000-$75,000+
3. NGOs, Charities, and Development Work
Organizations like Amnesty International, Red Cross, Doctors Without Borders, and smaller NGOs actively hire BAMES graduates for program management, research, advocacy, and field coordination roles.
Typical Roles:
- Program Officer
- Research Associate
- Advocacy Coordinator
- Field Representative
Average Salary: $40,000-$65,000
4. International Business and Finance
The MENA region is economically significant, with major investments in banking, energy, real estate, and technology. Companies need professionals who understand local markets, regulations, and cultural contexts.
Typical Roles:
- Business Analyst
- Market Research Analyst
- Compliance Officer
- International Trade Specialist
Average Salary: $50,000-$85,000+
5. Government and Intelligence
U.S. government agencies (State Department, CIA, FBI, Defense Intelligence Agency) actively recruit BAMES graduates for intelligence analysis, policy research, and international security roles. Arabic language proficiency is a critical advantage.
Typical Roles:
- Intelligence Analyst
- Policy Analyst
- Regional Specialist
- Security Consultant
Average Salary: $60,000-$95,000+ (varies by agency and clearance level)
6. Education and Academia
Universities and international schools hire BAMES graduates as teachers, instructors, and teaching assistants. Advanced degrees (MA/PhD) open paths to research and faculty positions.
Typical Roles:
- High School Teacher (Middle East/Arabic/History)
- University Instructor
- Curriculum Developer
- Academic Researcher
Average Salary: $45,000-$75,000 (teachers); $60,000-$100,000+ (professors with advanced degrees)
7. Translation and Interpretation
With language skills as a cornerstone of the degree, BAMES graduates can pursue professional translation/interpretation careers for government, NGOs, corporations, and media organizations.
Typical Roles:
- Translator
- Court Interpreter
- Conference Interpreter
- Translator (Document/Written)
Average Salary: $40,000-$70,000+ (varies by specialization)
Critical Factor: Language Proficiency
This cannot be overstated: Language fluency is the single most important differentiator for BAMES graduates in the job market.
Students who achieve advanced proficiency in Arabic (or another regional language) have dramatically better career prospects than those with basic conversational ability. Employers specifically look for candidates who can:
- Read and analyze complex texts
- Conduct interviews and negotiations
- Understand cultural nuances and idioms
- Translate documents and media
Action Item: Many universities partner with study-abroad programs in Jordan, Morocco, Oman, Lebanon, and the UAE. Spending a full semester or year immersed in Arabic-speaking environments accelerates language acquisition and significantly enhances career prospects.
BAMES vs. Master’s Degree: Which Should You Choose?
Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies
Pros:
- Builds foundational knowledge and language skills
- Lower cost and shorter duration (4 years vs. 2-3)
- Direct entry into entry-level positions
- Good for exploring if graduate study is your goal
Cons:
- Limited for government/intelligence positions (master’s often required)
- Lower starting salary than master’s holders
- More competition in job market without specialization
Best for: Students exploring the field, those interested in business/journalism, or those planning to pursue further studies.
Master of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies
Pros:
- 100% employment rate (recent data)
- Higher starting salary ($70,000+ vs. $58,000)
- Required for many government/diplomatic roles
- Typically 1-2 years (especially UK programs)
- Intense specialization in research/policy
Cons:
- Higher cost ($25,000-$70,000+ tuition)
- Requires bachelor’s degree + application
- More competitive admissions
Best for: Career changers, those targeting government/diplomacy, and professionals seeking specialization.
Career Trajectory: Many successful professionals complete a BA first, work 1-2 years to clarify career goals, then pursue a master’s. This path provides clarity and often leads to employer-sponsored education.
Scholarships and Financial Aid for International Students
University-Specific Scholarships
Georgetown University (Arab Studies)
- Various merit-based scholarships
- Application required
University of Exeter
- International scholarship funds
- Entry requirements: Academic excellence + demonstrated interest
SOAS, University of London
- Merit scholarships for MA students
- Partial tuition waivers available
US Public Universities
- Automatic scholarships for strong international students
- Eligibility: GPA 3.5+, test scores
Government Scholarships
- Turkish Government Scholarships for study in Turkey
- Qatar University Scholarships for undergraduate studies
- Israeli Government Scholarships for international students
- UAE Scholarships through Khalifa University and Abu Dhabi University
Private Scholarships
- Fulbright Program (varies by country)
- MENA-focused foundations (Arab American Institute, etc.)
- Language scholarships through State Department
Financial Aid Strategy
For international students without home country scholarships:
- Apply to generous universities (US public universities often offer more aid than Ivy League)
- Look for scholarships specifically for international students from your country
- Consider UK programs (3-year duration = lower total cost despite high annual fees)
- Explore work-study programs at universities
- Apply for external scholarships from cultural organizations
Study Abroad Opportunities
Most BAMES programs strongly encourage (or require) study abroad semesters. Popular destinations:
Arabic-Speaking Countries:
- Jordan (particularly Amman – safest, most established programs)
- Morocco (especially Fez and Rabat)
- Oman (emerging hub for language study)
- UAE (Dubai and Abu Dhabi – modern facilities)
- Lebanon (Beirut – for advanced learners)
Benefits of Study Abroad:
- Accelerated language learning (3 months abroad = 1 year classroom study)
- Cultural immersion
- Networking with regional professionals
- Resume enhancement for employers
- Personal growth and perspective
Cost: Typically $10,000-$25,000 per semester (included in some programs, separate cost for others)
Essential Skills Employers Value
Beyond subject knowledge, employers hiring BAMES graduates specifically seek:
Hard Skills
- Arabic language (advanced proficiency)
- Research and data analysis
- Report writing
- Cross-cultural communication
- Policy analysis
- Project management (for NGO roles)
- Microsoft Office, Google Workspace
- Database management
- Social media and digital communications
Soft Skills
- Critical thinking (analyzing multiple perspectives)
- Adaptability (working in complex environments)
- Communication (articulating complex ideas clearly)
- Problem-solving (addressing cross-cultural challenges)
- Teamwork (multinational teams)
- Resilience (managing frustration in challenging regions)
- Cultural intelligence (navigating different contexts)
How to Build These Skills
- Language immersion: Study abroad for maximum impact
- Internships: Seek positions with NGOs, government, media
- Research projects: Conduct original analysis for class/thesis
- Leadership roles: Student organizations, clubs
- Tech proficiency: Data analysis, social media management courses
- Networking: Conferences, professional associations (MESA: Middle East Studies Association)
BAMES Degree in the Job Market: Reality Check
What Works
✓ Arabic language proficiency – Opens doors across sectors
✓ Geographic expertise – MENA region remains strategically important
✓ Interdisciplinary skills – Adaptable to multiple career paths
✓ Government demand – State Department, intelligence agencies actively recruit
✓ International organization positions – UN, World Bank, NGOs value regional specialists
Common Challenges
✗ “Too general” without specialization – Pairing with a minor (economics, security studies, business) strengthens marketability
✗ Language fluency requirement – Basic conversational Arabic isn’t enough for most professional roles
✗ Competition – Large number of BAMES graduates pursuing limited diplomatic positions
✗ Geographic constraints – Some employers require willingness to relocate to MENA region
✗ Bachelor’s level limitations – Master’s degree often required for advanced positions
Strategies for Success
- Achieve advanced language proficiency (non-negotiable)
- Add a complementary minor (economics, business, international relations)
- Pursue internships (government, NGO, media)
- Build a network through study abroad and professional conferences
- Plan for graduate school early (pursue MA if targeting government/diplomacy)
- Develop additional expertise (security studies, climate/environment, gender studies)
How BAMES Fits into Career Transitions
BAMES is an excellent degree for career changers and those seeking to shift into international affairs. Some examples:
- Engineering → International Development: Engineer with BAMES insight can work on development projects
- Business → International Relations: Business professional with MENA expertise enters corporate international affairs
- Journalism → Foreign Correspondent: Journalist with BAMES background becomes region-specific expert
- Law → International Law: Law student complements JD with BAMES knowledge for international legal practice
Graduate School Compatibility: BAMES graduates also pursue:
- Law School (LLB/JD)
- Business School (MBA) – especially with Middle East focus
- Public Policy (MPA/MPP)
- International Relations (MA/MS)
- Development Studies (MA/MS)
International Student Considerations
Visa and Work Authorization
United States:
- F-1 visa for international students
- Optional Practical Training (OPT): 12 months post-graduation
- Possible extension for STEM designation in some programs
- Employer sponsorship pathway to green card
United Kingdom:
- Student visa during studies
- Post-Study Work Visa: up to 2 years after graduation
- Path to sponsorship from UK employer
- EU/Commonwealth citizens have separate regulations
Middle East Countries:
- Sponsorship typically through employer
- Student visas available but limited
- Work regulations vary by country (UAE more open, others restrictive)
Language of Instruction
Most international BAMES programs taught in English. Regional universities in Middle East often teach in Arabic with English electives.
Cultural Adjustment
Moving to study in Western universities: MENA students generally find welcoming environments at major universities. Check for:
- Islamic student societies
- Arabic-speaking student communities
- Diversity and inclusion policies
- Mental health and cultural support services
Real-World Success Stories
Profile 1: From BAMES to Diplomacy
Student: Sarah (US citizen)
University: Tufts University
Path: BA BAMES + Study abroad (Jordan) → MA International Relations → US State Department
Outcome: Foreign Service Officer in US Embassy in Cairo. Salary: $75,000+ with benefits. 8 years post-graduation.
Profile 2: NGO and Development Work
Student: Ahmed (Egyptian international student)
University: University of Manchester
Path: BA Middle Eastern Studies → Internship at IRC (International Rescue Committee) → Full-time position
Outcome: Program Officer managing refugee services in Lebanon. Salary: $50,000 + housing stipend. 5 years post-graduation.
Profile 3: Media and Journalism
Student: Lisa (German citizen)
University: SOAS
Path: BA Middle Eastern Studies → MA Journalism → Freelance journalist + BBC
Outcome: Correspondent covering MENA region. Mixed freelance/contract income: $60,000-$80,000+ annually. 7 years post-graduation.
Profile 4: International Business
Student: Omar (Saudi Arabia)
University: University of Pennsylvania
Path: BA Middle Eastern Studies + Economics minor → Management consulting firm
Outcome: Consultant specializing in MENA market entry strategies. Salary: $70,000 starting + bonuses. 3 years post-graduation.
Common Questions About BAMES
Q: Do I need to know Arabic before starting?
A: No. Most programs assume zero prior knowledge. However, strong language learning aptitude helps significantly.
Q: Can I complete a BAMES degree online?
A: Limited options exist, but most programs require in-person attendance. Some universities offer hybrid models. Study abroad is difficult to complete virtually.
Q: How difficult is the degree?
A: Moderate to challenging. Heavy reading and writing requirements. Language study is intensive but manageable. Most motivated students succeed.
Q: What if I want to study a specific MENA country (Israel/Palestine, Iran, etc.)?
A: Most programs offer country-specific modules. Discuss specialization options with advisors. Study abroad in your country of interest strengthens expertise.
Q: Is there a competitive job market for BAMES graduates?
A: Yes, but solvable. Language proficiency + internships + networking = strong candidacy. Master’s degree significantly improves prospects for government/diplomatic roles.
Q: Can I work in the Middle East with a BAMES degree?
A: Yes, but typically requires employer sponsorship or NGO assignment. Most professional expat jobs require Arabic fluency and specific expertise. Teaching English is more accessible entry.
Q: What’s the difference between Middle Eastern Studies and Arabic Studies?
A: Middle Eastern Studies = broader regional focus across languages/cultures. Arabic Studies = deeper focus on Arabic language, culture, and literature. Many programs combine both.
Final Recommendations
If You’re Considering BAMES:
- Honestly assess language learning commitment. This degree demands substantial language study. If you’re not genuinely excited by language learning, reconsider.
- Research specific universities carefully. Program quality, resources, study abroad opportunities, and alumni networks vary significantly.
- Start internships early. Summer internships in Year 1-2 build experience and clarify career direction.
- Plan for graduate school. Many successful BAMES professionals complete a master’s degree. Budget and plan accordingly.
- Build a complementary expertise. Economics, business, security studies, or development studies minor maximizes career flexibility.
- Network actively. Join MESA (Middle East Studies Association), attend conferences, connect with alumni. Personal relationships often lead to opportunities.
- Gain study abroad experience. Full semester/year immersion dramatically improves language skills and career prospects.
Best Fit for BAMES:
- Intellectually curious about global affairs
- Comfortable with ambiguity and complex international issues
- Strong analytical and writing skills
- Genuine interest in languages (especially Arabic)
- Flexibility about career path
- Interest in international development, diplomacy, journalism, or business
Not the Right Fit:
- Seeking guaranteed specific job upon graduation
- Avoiding language study
- Wanting purely technical/STEM career
- Preferring straightforward career progression
- Limited budget for graduate studies if pursuing government roles
Conclusion
A Bachelor of Arts in Middle Eastern Studies opens doors to fascinating, meaningful careers across diplomacy, international development, journalism, business, and government. With realistic salary potential of $58,000-$76,000+ and strong employment prospects, especially with advanced language proficiency and a master’s degree, BAMES is a solid choice for globally minded students.
Success in this field depends on:
- Achieving advanced language proficiency
- Gaining practical experience through internships
- Possibly pursuing advanced education (MA/MS/MBA)
- Building professional networks
- Developing complementary expertise
The world needs informed professionals who deeply understand the Middle East and can bridge cultural and political divides. If you’re willing to invest in language learning, embrace intellectual challenge, and remain flexible about career outcomes, a BAMES degree positions you uniquely to contribute meaningfully to global affairs.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.